This article is based on Abhishek’s brilliant talk at the 2024 Product Marketing Summit in Seattle. As a PMA member, you can enjoy the complete recording here.
I'm here to talk to you about some esoteric technology that you've probably never heard of.
Just kidding! This article is all about AI. There’s a good chance you’re already using AI-powered tools at work every day – but are you using them as effectively as you could be?
Over the last year and a half, I’ve been working with AI and have discovered lots of hacks, tips, and tricks, which I’m excited to share with you.
Here’s a taste of what we’ll cover:
- The major advantages and challenges of AI
- How to navigate the vast array of AI tools and choose the ones that matter
- A look at how AI models work and the importance of prompt engineering
- The six key elements of effective prompts
- Examples and techniques for crafting prompts that deliver the best results
- Advanced prompting strategies to elevate your AI-powered content creation
Let’s dive into it, shall we?
AI: A massive time saver with some challenges
Looking at the stats, it’s clear that AI is a huge time saver. Salesforce conducted a study that found marketers expect to save up to five hours a week using AI.
As the technology advances, we can expect even more time savings. AI is not just about faster content production; it's also a game-changer for personalization. Many of us are already using it to translate content or create personalized social media posts.
AI models are also becoming more capable of analyzing large datasets. I’ve personally used AI for market research, extracting insights from data tables, conducting keyword research, and analyzing campaigns. For tasks like these, AI can be highly effective.
But let’s not ignore the challenges. One of the biggest issues is accuracy. For instance, if you have two product names that sound similar, AI might pick up one over the other without any distinction. And let's be honest – we’re all still figuring out what AI can and can't do, so there's definitely room for learning.
Navigating the deluge of AI tools
I was at a conference in San Francisco recently, and a VC mentioned that they get pitched around 1,000 new AI products each month, with many of these being marketing-focused.
That’s a crazy number of products, right? It can feel impossible to make sense of all these tools. The examples below are just a small sample of the AI marketing applications available – it's by no means comprehensive. And every single day, dozens of new products are launched on platforms like Product Hunt.
So, how many tools do you actually need? In my opinion, fewer than you might think. The underlying models, such as ChatGPT and Claude, are evolving so quickly that any tool you use today could be obsolete tomorrow.
After experimenting with many different tools, I now generally interact directly with the models themselves, rather than using marketing tools that harness their capabilities. Here’s why:
- Flexibility and control: Most marketing tools are just wrappers built on top of models. When you work directly with the model, you have more flexibility and control over the outcomes compared to using a tool that's essentially making an API call on top of the model. I’ve used various AI writing tools and found that working directly with models like ChatGPT generally produces slightly better results.
- Tools become obsolete quickly: Vendors often claim that their tools offer more complete capabilities, and while that may be true at the moment, the rapid evolution of AI models means that tools can become obsolete almost overnight. That’s why I prefer sticking to the models themselves.
- Direct interaction with models: Many of the latest models are available on platforms like Hugging Face or other repositories. There are now more tools that let you directly interact with cutting-edge models, and most of these models have user interfaces, so you don’t need to rely on third-party tools.
So, my advice is to work directly with the models where possible.
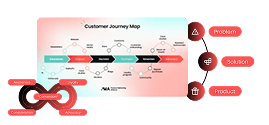
How AI models work
After working with neural networks for the last six years, I can say that understanding how models function is crucial for maximizing their potential. This Image below actually gives a pretty accurate explanation.
Essentially, these models are trained using millions or even trillions of tokens, words, and internet-scale data. This data is converted into weights, which are then stored within the model. Models have their own latent memory and understanding, learning patterns and relationships from the tokens fed into them.
The output these models generate depends on three key factors:
- The model itself: The structure and training of the model play a significant role in the output.
- The data: This includes both the data fed into the model externally and the data that lives within the model.
- The prompt: Sometimes, the prompt and the data overlap, making the quality of the prompt incredibly important.
This brings us to an essential point: learning how to prompt effectively is a skill worth mastering. As AI models continue to evolve, prompt engineering will be key to staying competitive in product marketing. Your ability to use prompts effectively will determine how well you can leverage these models for your strategies.
The six key elements of effective prompts
After spending a lot of time studying prompt engineering over the past year, I've identified six key elements of effective prompts:
- Task
- Context
- Persona
- Tone
- Examples
- Format
Including these elements can significantly enhance the quality and relevance of the output you get from AI models.
The first three elements – task, context, and persona – help in creating personalized outcomes. They set the foundation for generating on-point content that aligns with your goals. The remaining elements – tone, examples, and format – further refine the output, ensuring consistency and adherence to the desired result.
Now, let’s explore each of these elements in more detail and look at some examples of how to use them to build an effective prompt.
1. Task
This is the most basic element and where most people start when using models like ChatGPT. The task defines the action you want the model to perform. It's a straightforward way to begin using prompts and is essential in every prompt you craft.
2. Context
Providing context is about fleshing out the task with more background information and constraints. In marketing, this often includes details about the target audience, their needs, and preferences, or a specific use case.
3. Persona
Assigning a persona to the model has proven surprisingly effective. Starting your prompt by defining a persona, such as "You’re a seasoned product marketer" or "You’re a copywriter specializing in punchy, memorable lines," often leads to more tailored and effective outcomes.
4. Tone
Tone acts as an additional layer that shapes the style, voice, and emotion of the output. For instance, in formal business writing, you might specify a tone that’s "credible and conservative" rather than overly cheerful. Including a tone qualifier in your prompt can lead to higher-quality outputs that align with your brand’s voice.
5. Examples
Think of the model as a brilliant five-year-old – it knows a lot but sometimes needs guidance to understand exactly what you want. While you can ask the model to write in a particular way, it often struggles to fully adhere to your instructions without clear examples. So, providing examples is extremely useful, especially when specifying tone or style.
The number of examples you provide can vary; based on the reports I've read, anywhere from five to twelve examples can be quite effective. When creating custom GPTs, uploading 15 to 20 pieces of content can help the model produce on-point outputs.
6. Format
Format is crucial for structuring the output, saving you time in editing. You can specify whether you want the output in bullet points, numbered lists, or markdown format, and you can even ask the model to avoid opening or closing statements if they’re not needed. Defining the format helps you get clean, usable results right from the start.
Putting it all together: Sample prompt
Now that we've gone through the elements, let's put them together into a sample prompt. By combining the task, context, persona, tone, examples, and format, you can guide the model to generate content that’s closer to your final desired outcome.
Generate a list of 10 attention-grabbing subject lines for our email marketing campaign promoting our new line of eco-friendly outdoor gear. The subject lines should convey the eco-friendly nature of our products while also highlighting their durability and functionality for activities like hiking, camping, and rock climbing.
Here are two examples of attention-grabbing subject lines we've used before: 'Gear Up for Adventure: Our Toughest (and Greenest) Line Yet' and 'Nature's Calling: Answer With Our Eco-Warriors Collection.'
Please provide the subject lines in a simple numbered list format. Use an adventurous, energetic tone that sparks a sense of excitement and wanderlust in the reader."
Takeaways and next steps
Experimentation is key to getting the right outputs. By using different combinations of the six elements we discussed and trying out various models, you can get to workable solutions pretty quickly.
What I’ve just outlined is the basic prompting strategy – where all the context is fed into a single prompt and given to the model. But, as you get more comfortable, you’ll likely start exploring more advanced prompting strategies. These include "zero-shot", "few-shot", and "chain of thought" techniques, which I’ve found incredibly useful lately.
There’s a whole world of advanced techniques out there, and using a combination of them leads to much higher-quality content and outcomes.














 Follow us on LinkedIn
Follow us on LinkedIn



.svg?v=1abcb94374)